The Future of Mega Heat Pumps
Decarbonizing heat is more urgent than ever. In this video, Everllence expert Mikael Adler explains how mega heat pumps and turnkey solutions are reshaping sustainable, CO₂‑neutral heating worldwide.
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Facts
Good to know
Maximum temperature that can be supplied by Everllence heat pumps
CO2 emissions from a heat pump running on renewable energy
households can be provided with zero-emission heat by a 70 MW heat pump solution
Decarbonize your business with Everllence heat pumps
Heat pumps play a crucial role in the journey towards sustainable heat supply solutions for both businesses and communities. By eliminating the need to burn fossil fuels for heating and cooling, they instead use the potential of various heat sources, including lakes, rivers, seawater, wastewater, industrial waste heat, geothermal energy, and ambient air. Alternatively, heat pumps can be powered by electricity derived from renewable sources, ensuring a completely carbon-neutral heat supply.
When choosing the Everllence heat pump system, you gain access to the most advanced large-scale heat pump technology available. A heat pump extracts heat from a low-temperature source like water, air, or waste heat from machinery, amplifies it to a useful high temperature, and transfers it to where it is needed. The principle is based on a closed-loop refrigerant cycle with compression and expansion of the fluid, and can be operated in both directions to deliver heating or cooling. Powered by renewable electricity, the heat pump can supply carbon-neutral heating or cooling.
Find the right heat pump for your application
Everllence heat pumps
Our industrial heat pump solutions make efficient use of manifold heat sources. Running on green electricity, they have virtually zero emissions. In addition, we concentrate on eco-friendly coolants. These large-scale heat pumps are comprised of compressors, expanders, and companders.
Everllecnce heat pumps can be used in versatile ways and tailored to the special needs of customers: The temperature supply range of 60 - 300°C is suitable for heating water and liquids, process and district heating, or steam production. The power output ranges from 10 megawatts thermal (MWth) to above 100 MWth per heat pump unit. Higher outputs can be achieved with several heat pumps in parallel operation.
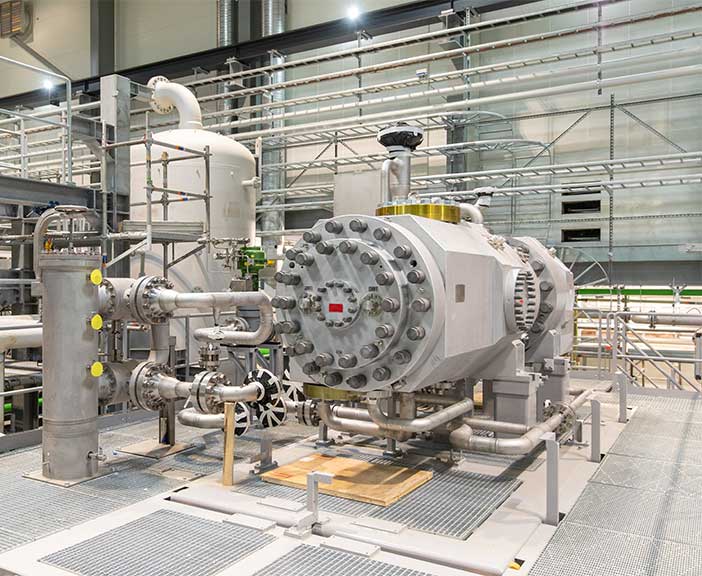

Heat pumps for industrial use at a glance

Energy producers and process industries
Future fuels are available to defossilize your industry. We provide everything you need to produce e-fuels,
whether you are an independent power producer or an industrial
manufacturer. Our scalable reactor modules let you manufacture liquid
and gaseous fuels – putting you at the
vanguard of energy independence and sustainability.
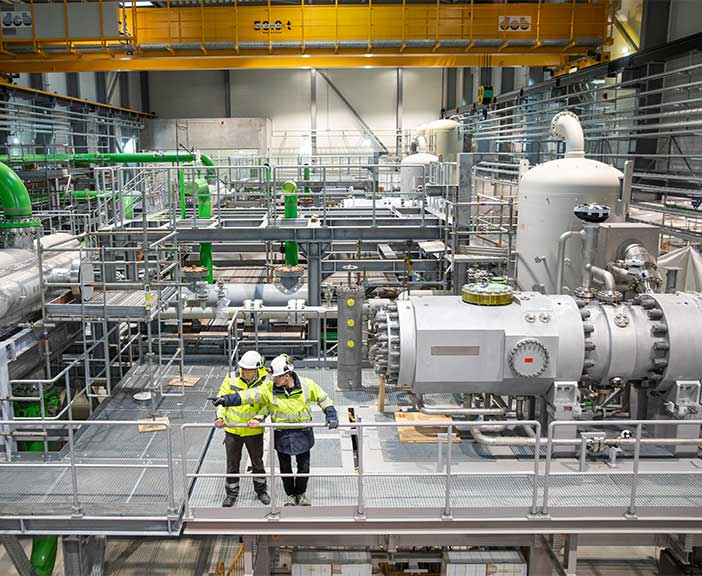
Compressor expertise
The heart of the heat pump is the compressor. We have decades of experience
in developing compressors for the most demanding conditions. Our wide
range of designs ensures we can tailor each pump to the customer’s
specific power, temperature, and space requirements.
Our
high-temperature heat pumps bring the economic and climate-friendly
benefits of domestic heat pumps to large-scale industrial applications.
To ensure a process steam supply, we can offer a combined heat pump / vapor compressor or a separate vapor compressor skid that provides the required process conditions.
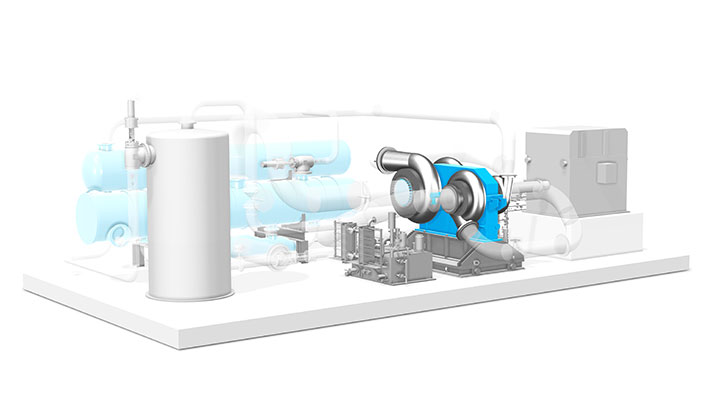
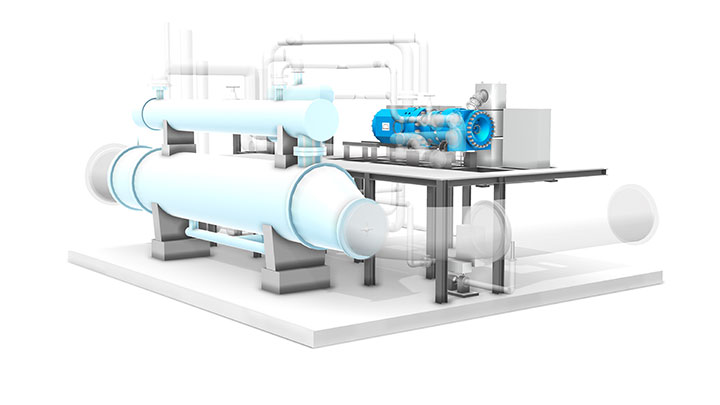
Requirements
Heat pumps require a heat source in addition to electricity from a grid. The external heat source provides the energy to generate the thermal power output – which is many times higher than the electrical power input. To achieve performance, water or other liquid energy sources are utilized. Oceans, rivers, or lakes can all serve as such a source.
The entire process becomes even more efficient and environmentally friendly when industrial waste heat is used. When available, geothermal energy is also a good heat source. The system is scalable, site-independent, has a minimal environmental impact, and can be tailor-made for specific applications.
Applications
Scalability and modularity make heat pumps suitable for many applications:
- Process industries
(including chemicals, petrochemicals, metal, food & beverages,
paper, wood, rubber & plastic, textile, machinery & equipment)
can enjoy cost-efficient carbon-neutral energy for industrial processes
that require intensive heat, cold, and electricity.
- Municipal, urban, and large facilities can provide district heating and warm water for urban quarters, small towns, and large facilities like airports, universities or shopping malls.
- Data centers can reduce CO2 emissions and
electricity costs with a direct supply of cooling energy. Participating
in the power markets opens up new revenue streams.
- Power producers and utilities can balance the supply and demand of renewable energy while providing hot and cold thermal energy.


A single enormous heat pump for an entire city
Green heat for the Danish city Esbjerg
A single Everllence heat pump solution has the potential to decarbonize an entire city by supplying climate-neutral heat via its district heating network – without the need to install various small-scale heat pumps in each single home. Here’s how we already make it a reality:
The Danish port city Esbjerg aims to become carbon-neutral by 2030 and is transforming major infrastructure to achieve this goal. The city will decarbonize its district heating supply using heat pump technology from Everllence to replace a coal-fired system.
Everllence has supplied an industrial heat pump solution which will supply 280,000 MWh of green heat to overall 100,000 inhabitants via the city’s district heating network – annually saving 120,000 tons of CO2 emissions
Frequently asked questions
When we talk about climate change, the focus often falls on electricity generation, but heating and cooling account for almost 40 percent of the world’s carbon emissions. The sector is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels and is at the beginning of its decarbonization journey. Heat pumps, instead of burning fossil fuels, make efficient use of heat sources such as lakes, rivers, sea, wastewater, industrial waste heat, as well as geothermal or ambient air. Another option is to use electricity from renewable resources to drive the heat pumps, which makes the heat supply completely carbon-neutral
Most of the challenges are economic. Though heat pumps require an initial investment, their value comes from capturing the energy that would otherwise be wasted or has to be produced separately. The profitability is directly related to the temperature of the heat being used — the lower the temperature, the higher the profitability. Heat pumps have specific needs in order to effectively couple sectors. Among the most important requirements is the proximity to a reservoir that can absorb heat, usually a large body of water.
On average, well-maintained heat pumps can last anywhere 30 years or more. Proper maintenance, including routine inspections, can help extend the heat pump’s lifespan and ensure it continues to perform efficiently.
Selecting the appropriate capacity of an industrial heat pump is crucial to ensure it meets the specific needs of your application. Factors to consider include the size of the space to be heated or cooled, the required temperature range, the available heat source, and the heating or cooling load. An oversized or undersized system can lead to inefficiency and increased operating costs. Do not hesitate to contact us for consultation!
To maintain the optimal performance of an industrial heat pump, regular maintenance is essential. This includes scheduling routine inspections, cleaning filters and heat exchangers, checking for refrigerant leaks, and ensuring that all components are in good working condition. Additionally, monitoring the system's energy consumption and performance can help identify issues early and optimize its operation.
