The sustainable power of mega heat pumps
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Facts
Good to know
suitable for heating liquids and steam production
thermal power output per unit
from heat pumps running on renewable energy
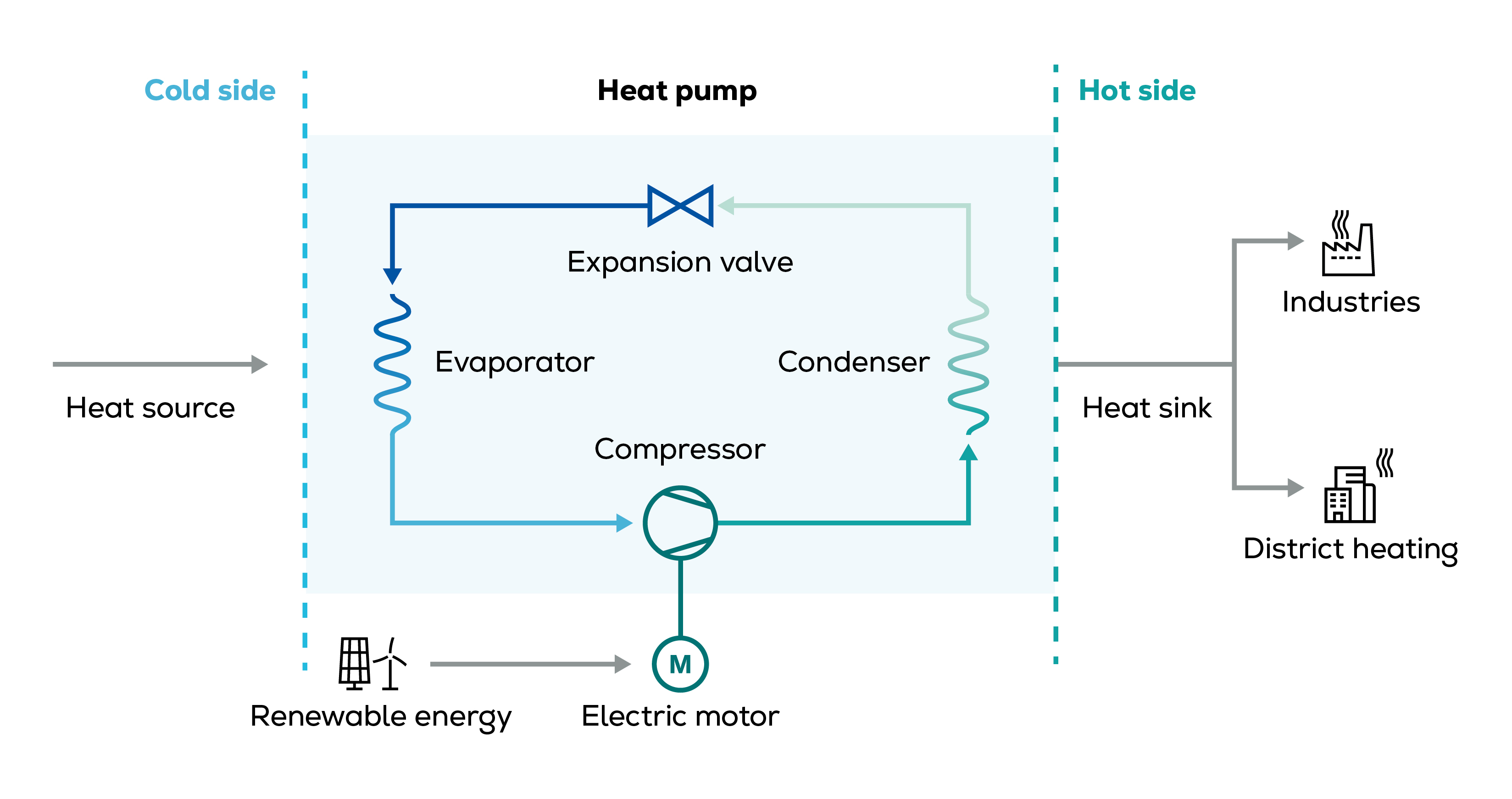
How it works: amplifying and transferring thermal energy
A heat pump extracts heat from a low temperature source – like water, air, or waste heat from machinery – amplifies it to a useful high temperature and transfers it to where it’s needed. The principle is based on a closed-loop refrigerant cycle with compression and expansion of the fluid and can be operated in both directions to deliver heating or cooling. Electricity is needed to power the compressor. Powered by renewable electricity, the heat pump can supply carbon-neutral heating or cooling.
Environmental sustainability
Heat pumps for district heating
The environmental, economic, and social benefits of district heating are greatly enhanced by using heat pumps. They enable you to reduce CO2 emissions, integrate renewables, offer grid balancing services, and make energy systems more flexible.


Economic efficiency
Heat pumps for industrial processes
Heat production accounts for about two-thirds of industrial energy consumption, with conventional production processes increasing emissions, operating expenses, and carbon taxes. Large-scale heat pumps produce efficient heat and steam, reducing your CO2 emissions and energy costs while making your processes more sustainable.
Added value supplied by your heat pump
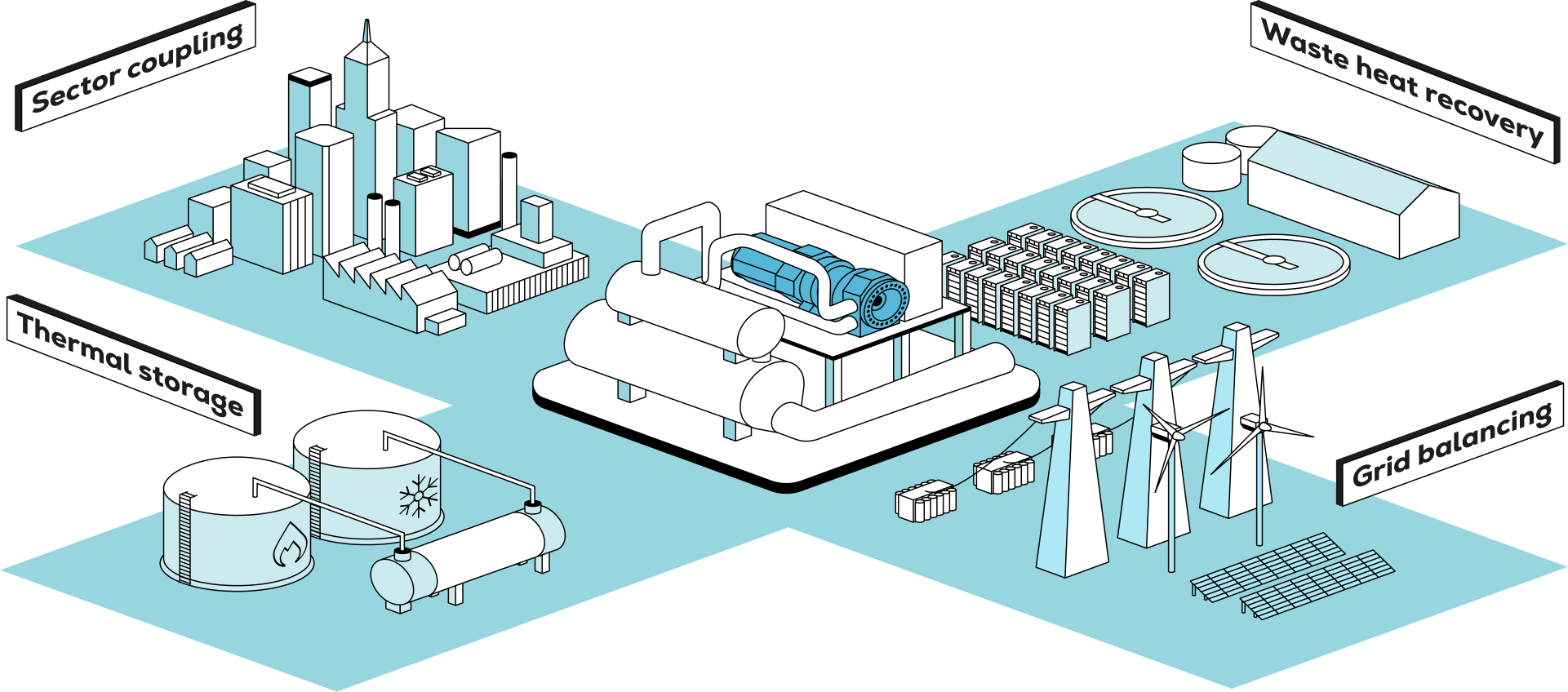
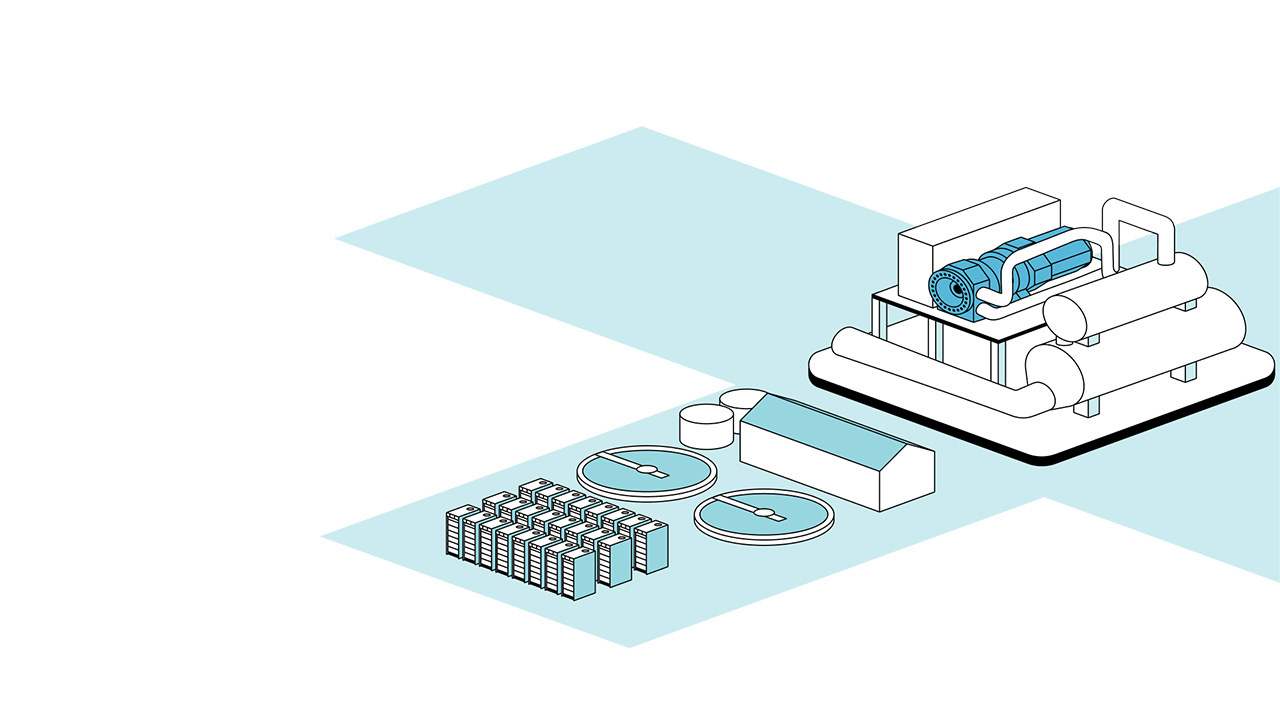
Connect electricity, heating, and cooling
Everllence Heat Pumps enable sector coupling by linking power generation, heating, and industrial demand. This unlocks flexible system use, better engergy flow, and new business potential from integrated operations.
Stabilize the grid with smart thermal energy use
By converting excess renewable power into usable heat, Everllence Heat Pumps help balance supply and demand. They contribute to grid stability and support a resilient, low-carbon energy system.
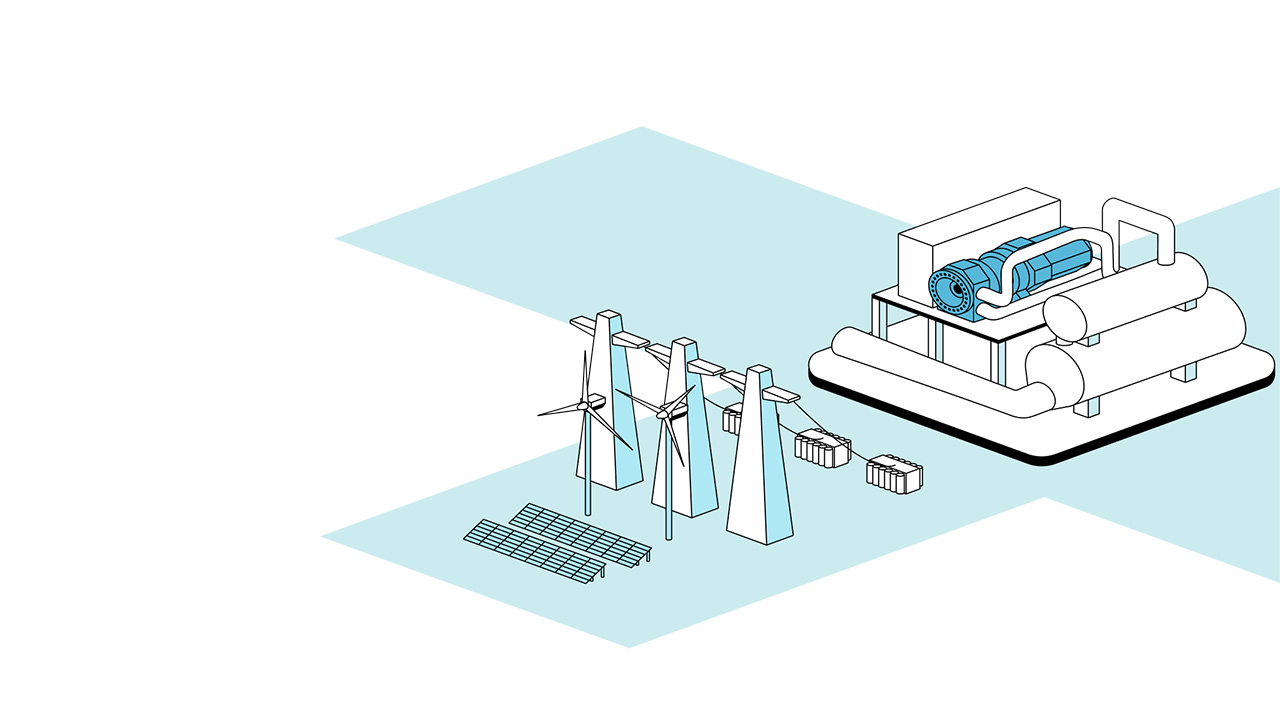
Storage engergy where and when it's needed
Everllence Heat Pumps store thermal energy as hot or cold water, making renewable energy usable even when supply and demand don't align. This flexibility supports stable, efficient operations across industries and utilities.
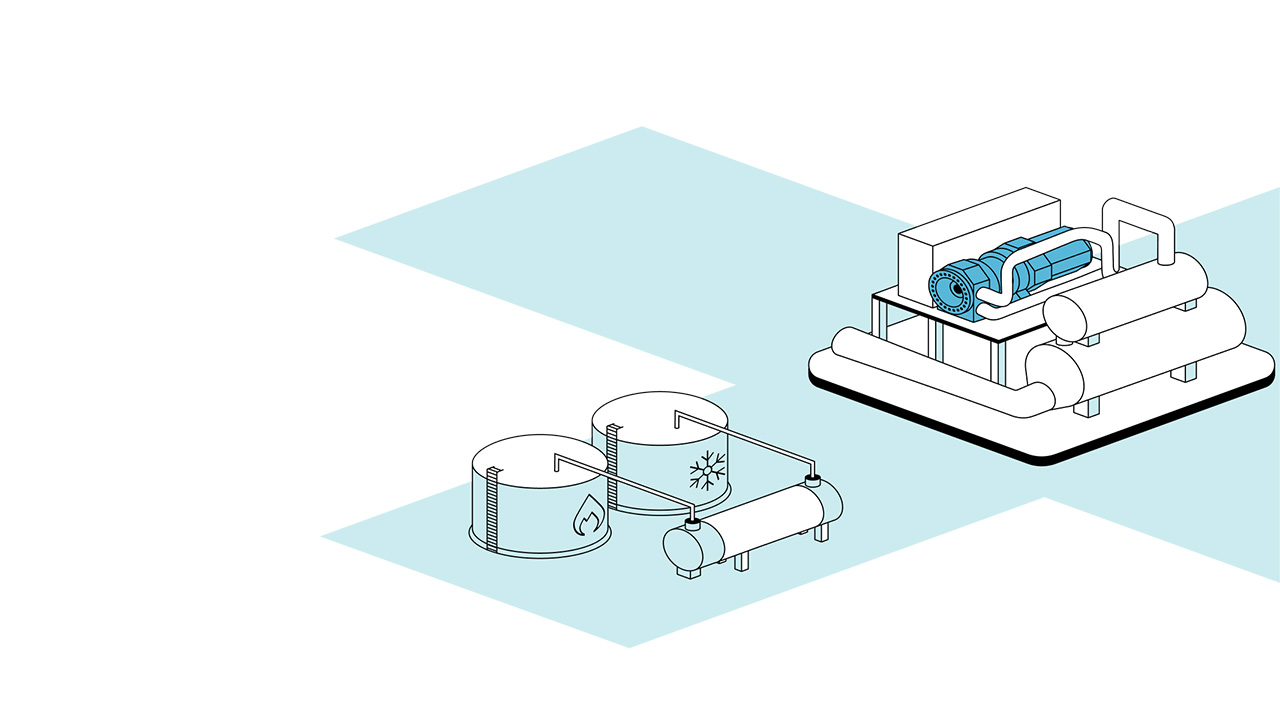
Unlock the value of your waste heat
Everllence Heat Pumps generate heating and cooling using renewable electricity or industrial wast heat - reducing emissions, increasing energy efficiency, and supporting decarbonized thermal applications.
Download
Whitepaper
Sector coupling with heat pumps
.jpg?sfvrsn=955ecfcf_1)
Stabilizing the grid with industrial heat pumps

Your heat pump is in expert hands
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Mikael Adler from Everllence about the future of mega heat pumps
Decarbonizing heat generation is more urgent than ever. The market for mega heat pumps is booming — and with countless large-scale projects on the horizon, their impact on sustainable, CO2-neutral heating will only grow. Everllence delivers optimal solutions, expert consulting, and turnkey execution for complex energy projects — all from a single source.
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
21st century - the age of the mega heat pumps
Mega heat pumps delivering unmatched solutions to today’s energy challenges. With no compromises on efficiency, sustainability, or economics, Everllence has secured groundbreaking projects across Europe. Investing in a mega heat pump means choosing long-term energy security and profitability.
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
Mega heat pumps will be absolutely decisive in achieving industrial climate targets
Mega heat pumps are a game-changer for climate action. As one of the only technologies that both decarbonizes and increases system efficiency, they directly address the core of industrial CO2 emissions. Everllence is unlocking their full potential — making industrial processes energy-efficient and climate-neutral at scale.
By loading the video you agree to YouTube's privacy policy.
The heat is on! Everllence’s first-of-its-kind mega heat pump solution in action
Everllence is reshaping the future of heat generation. From powering 25% of a Danish city’s heating needs to delivering the largest air-to-water heat pump in Helsinki and the biggest river heat pump in Cologne — our projects are setting new standards. With ultra-efficient systems and natural refrigerants that are safe for the environment, Everllence is driving the sustainable energy transition.
Contact our experts
Your business: your questions
Heating and cooling, emissions and costs, sizes and integration, COP and LCOH, technology etc. Whatever you want to know about heat pumps: ask our experts. At Everllence we have know-how and experience in a wide range of sectors including petrochemicals, food & beverages, pulp & paper, district heating, and carbon capture.

Downloads
Continue reading